Position: Technical Manager, Field: Analytical chemistry, Organisation: Cawthron Institute.
Paul McNabb worked as the Technical Manager at the Cawthron Institute in Nelson. This involved the management of a team of analytical chemists focused on research for industry. Usually this involves the analysis of new food and nutraceutical1 products.
Paul studied chemistry and biochemistry2 at Otago University. He then worked as a research assistant and completed an honours degree. Still not convinced he wanted to be an academic, he left for a stint of working and travelling, including a few months in London at a clinical laboratory. After returning to New Zealand and working some odd jobs, Paul became an analytical chemist3 with the Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries in Wellington. As a born and bred Nelsonian, he wanted to get back to the sun. Paul moved to Nelson and was able to continue his career at the Cawthron Institute.
Paul’s interest is in liquid chromatography4 in any form. He is especially interested in automated systems for the analysis of trace components in a range of biological samples. He has expertise5 in the coupling of HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) and UPLC (ultra performance liquid chromatography) to mass spectrometers in the form of modern liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry6 (LC-MS) systems.
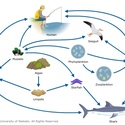
Most of Paul’s experience with LC-MS is with investigations of marine and freshwater toxins, usually produced by microalgae and found in shellfish. Some of these toxins are the target of international food regulations. Paul set up a testing laboratory at the Cawthron Institute to ensure New Zealand’s seafood is tested using the best possible science. New Zealand, the Cawthron Institute and the lab Paul established are now recognised as world leaders for the testing of toxins in shellfish. He traveled regularly to international conferences, and the work done at Cawthron has been published in papers, books and other media.
At the bottom of it is a fundamental understanding of biology7, so these studies will lead on to discoveries about biology that could be significant to other areas that we can’t imagine – areas like health and other scientific endeavours.
Paul continued to be involved in the routine testing of shellfish for toxins and acted as an advisor and mentor to the staff working in the routine testing laboratories at Cawthron. He worked on the source of tetrodotoxin8 (TTX9) in grey side-gilled sea slugs, trying to find out more about TTX’s occurrence in New Zealand’s coastal environment.
Paul enjoys outdoor pursuits, including mountain biking, running and multi-sport. Most of his free time is taken up with family life, school events, kids’ sports and concerts. He also spends time on things like house renovation or gardening – reluctantly. Paul’s dream is to sail into the Pacific for a couple of years. He regrets not wasting more time learning to play guitar.
In 2015 Paul left Cawthron and moved to IECU (Ion Exchange10 Cellulose11 Unit), which is part of Thermofisher, but still based in Nelson.
This article is based on information current in 2012 and updated in 2020.
- nutraceutical: A food or food product that has a beneficial effect on human health.
- biochemistry: A branch of science that studies how chemical processes occur in living things.
- chemist: A scientist trained in the science of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties.
- chromatography: A chemical technique used to separate different molecules in a mixture.
- expertise: Having excellent knowledge or skills in a particular area.
- mass spectrometry: An analytical technique measuring the characteristics of individual molecules by converting them to ions.
- biology: The science of living things.
- tetrodotoxin (TTX): A potent neurotoxin with no known antidote.
- tetrodotoxin (TTX): A potent neurotoxin with no known antidote.
- ion exchange: A reversible process where ions are swapped between different substances on the basis of their electrical charge.
- cellulose: A stringy and fibrous carbohydrate (a type of polymer made up of glucose molecules) that is the main constituent of the cell walls of plants, especially important in wood, cotton and hemp etc. Used in the manufacture of paper, cotton and other textiles, kapok, cellophane, rayon, explosives and some pharmaceuticals.