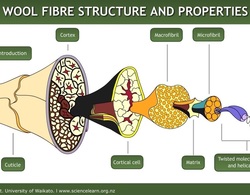
The cortex – the internal cells - make up 90% of the fibre. There are 2 main types of cortical cells – ortho-cortical and para-cortical. Each has a different chemical composition. In finer fibres, these two types of cells form in two distinct halves. The cells expand differently when they absorb moisture, making the fibre bend - this creates the crimp in wool. In coarser fibres, the para-cortical and ortho-cortical cells form more randomly so there’s less crimp.
Fibre crimp makes wool feel springy and provides insulation by trapping air.
Image: University of Waikato